Hemp-Based Composite Could Facilitate Soil-Free Farming
Given the diversity of its applications, hemp has become an increasingly popular crop in the United States and elsewhere over the past half-decade. That increasing production has led to surges of an appealing byproduct: hemp fiber.
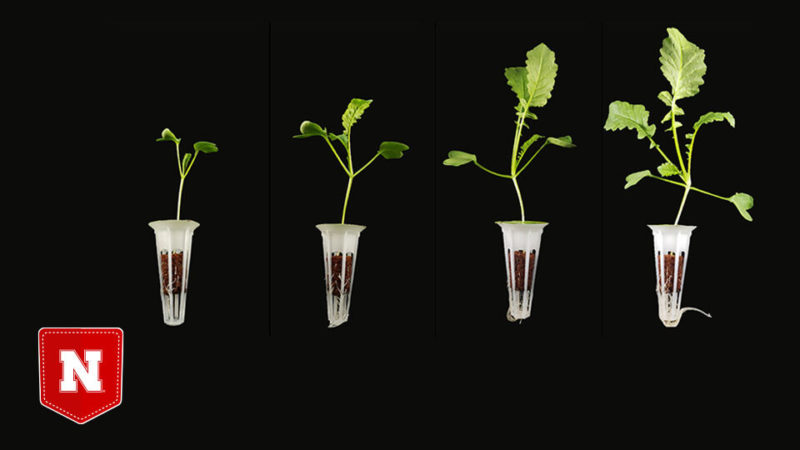
Mixing hemp fibers with other materials can form multifunctional biocomposites suitable for growing plants via hydroponics, a type of soil-free horticulture that substantially reduces land, water and pesticide use, among other benefits.
But hemp-based biocomposites can sometimes lack the mechanical strength needed to support proper plant growth. And current chemical methods developed to improve the structural integrity of those biocomposites usually produce volatile organic compounds, or VOCs, that are harmful to health and the environment.
 Nebraska chemist Barry Cheung and his colleagues recently introduced an approach that chemically couples a structure-granting component of hemp fibers, lignin, with “linking molecules” that fortify the resulting biocomposite. Unlike prior techniques, the team’s approach requires only water as a solvent, yielding harmless inorganic salts rather than VOCs as byproducts.
Nebraska chemist Barry Cheung and his colleagues recently introduced an approach that chemically couples a structure-granting component of hemp fibers, lignin, with “linking molecules” that fortify the resulting biocomposite. Unlike prior techniques, the team’s approach requires only water as a solvent, yielding harmless inorganic salts rather than VOCs as byproducts.
Mechanical testing revealed that the new biocomposite is more durable than a standard hemp-based counterpart, holding its shape far better when subjected to compressive forces. It can also hold roughly twice as much water as pure hemp fiber, putting its capacity nearly on par with commercial peat moss.
The team proceeded to grow both Daikon radishes and green peas from the biocomposite, a promising sign for its potential as a viable, eco-friendly growth medium.
Applying the chemical technique to other lignin-containing fibers — including flax, jute and coconut husk — could produce a suite of sustainable biocomposites for use in growth media, bioplastics and packaging materials, the researchers said.
Expanding that range of hydroponic growth media could prove especially important as the global population continues rising, water resources become scarcer, and the erosion of topsoil makes conventional farming more difficult.
Source: University of Nebraska-Lincoln