DLI ‘Requirements’
The DLI refers to the daily light integral, which simplistically is the total amount of photosynthetic light delivered to plants each day. More technically, it is the integrated photon flux density between 400 and 700 nm received in 1 square meter (m2) per day (d). The unit is mol·m–2·d–1 or more simply, moles per day or mol/day. There is a good correlation between the average DLI and plant growth, meaning that plant growth increases fairly linearly with increases in DLI.
Growers sometimes ask for the DLI “requirement” of a particular crop, or type of crops. In my opinion, there is no such thing as a DLI requirement because, with some notable exceptions, most plants can grow under a wide range of environmental conditions, including different DLIs. Growth of crops also depends on carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration and especially temperature, as well as crop culture. Therefore, providing a DLI requirement is both subjective and situational.
The DLI is essentially the amount of energy given to a plant, which it can use to develop and maintain leaves, stems, roots, flowers, and fruits. Therefore, for most floriculture crops, plant quality increases with DLI; plants develop more branches, thicker stems, more and larger flowers, and more roots when grown under a high DLI than a lower one. Exceptions to this rule-of-thumb are shade plants such as foliage plants and phalaenopsis orchids, which cannot tolerate high light conditions. For fruiting vegetable crops such as tomato and cucumber, fruit number and size increase with DLI, especially when the air is enriched with CO2.
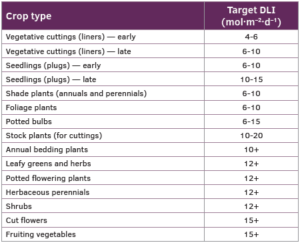
There are, however, DLI guidelines to produce plants of at least moderate quality, temperatures. The DLI values in Table 1 are generic and simplistic, and can be somewhat higher for plants grown at a high temperature and somewhat lower when grown at a lower temperature.
TOO LITTLE OR TOO MUCH
There are several potential consequences to floriculture crop production when the average DLI is less than the desired range. Examples include slow rooting during propagation, delayed flowering, weak branching, greater need for plant growth retardants, and low flower number. The DLI can be increased by cleaning or replacing greenhouse glazing, reducing or eliminating obstructions overhead (such as hanging baskets), and operating supplemental, high-intensity lighting. The use of low-intensity (screw-in) fixtures does not increase the DLI.
Conversely, there can be negative outcomes for some crops when the DLI is too high. Examples include leaf tip burn of some lettuces, cuttings harvested from stock plants that are reproductive, and foliage burn of plants that naturally grow in the shade. Decreasing the DLI is straightforward; the greenhouse can be shaded with whitewash or shading fabrics/screens, or crops that tolerate high light conditions can be hung overhead.
When the ambient DLI is low, the market and economics can influence the viability of increasing the DLI. Some markets may pay a premium price for a premium product, which can help make supplemental lighting of finished plants more economical. For young plants, propagation time can decrease substantially when a sufficient DLI is provided to seedlings or cuttings. Challenges in propagation, such as growth of algae, control of nutrition and pest control, are also reduced when propagation time is short.
Therefore, growers should focus on delivering at least the minimum recommended DLI to produce at least moderate quality crops and in a reasonably short period of time. For finished plants, more light is usually good, but increasingly the DLI beyond that minimum is often not economical unless the market commands a premium price. In contrast, it is often economical to increase the DLI almost year-round for fruiting vegetables because of continued increases in yield.









 Video Library
Video Library